Authors
Dr. Saurav Arora
Gold Medalist, MD (Hom.)
Founder: Vivid Homeopathy
Dr Saurav Arora has an experience of more than 15 years being a medical homeopath and independent researcher. Dr Arora has served various key positions in Ministry of AYUSH, Govt. of India; Ministry of Defence, India; Govt. of NCT of Delhi etc.Dr. Bharti Arora
Silver Medalist, MD (Hom.)
Founder: Vivid Homeopathy
Dr Bharti Arora has an experience of more than 10 years being a medical homeopath and consultant. Dr Bharti Arora is committed to promote homeopathy for the benefit of individual and health care system.Issued in Public Interest by www.vividhomeopathy.com
In This Issue
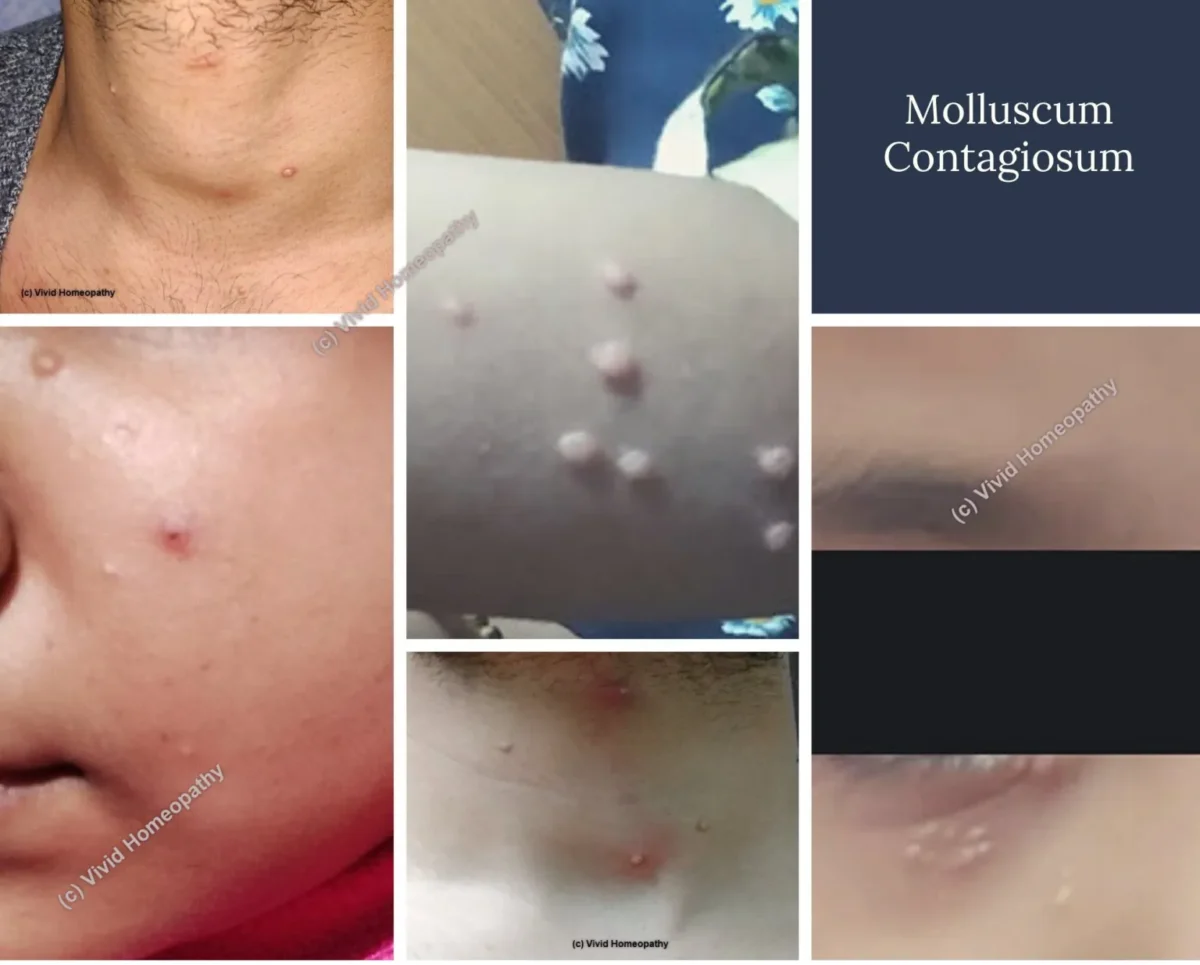
- Molluscum contagiosum.
- Presentation
- Effects on Health
- Spread
- Diagnosis & Differential Diagnosis
- Conventional Treatment
- General Management
- Role of Homeopathy in Molluscum Contagiosum
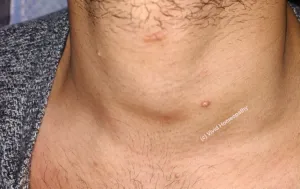
Molluscum Contagiosum
In an era where immunity is challenged to a larger extent, viral diseases are emerging as a large threat to human health. Even the rarest of viral disease are now heard very commonly. Due to increasing burden of environmental stress, decreasing immunity such diseases are expressing themselves in ever increasing form.One such common benign condition which is now being reported commonly in clinical practice is Molluscum contagiosum (MC). It is an infectious disease due to poxvirus (molluscum contagiosum virus). MC is considered to be a mild, benign skin disease but it is also a common medical and cosmetic burden to a patient who is suffering with it.
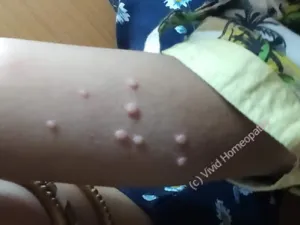
Presentation
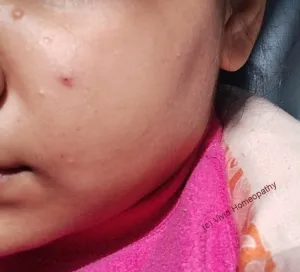
MC patient presents with lesions. The lesions are- Small to big,
- Shiny, smooth
- Raised – usually pink, white or skin coloured
The hall mark feature is the pitting in centre, and often we call it a pearl appearance.
The lesions can be very small or even large upto pea size and more, usually occurring on the body parts like face, neck, arms, shoulder, abdomen, genitals. The lesions can be in group or discrete.
Patient usually presents to a doctor when lesions itch, are red or become swelled up. Majority of the cases are either mis-diagnosed as warts, self treated, or left to heal on their own because of no complaints. The MC is more commonly present in young children and adolescents, but lately adults have also seems to be affected with this disease.
 Effects on Health
Effects on Health
While the eruptions are in incubation period, an individual may not have any symptoms at all. The initial symptoms include cosmetic concerns due to lesion especially on face, arms or any visible parts of the body. In few cases, especially in children, the matter of concern is the added infection or inflammation of the lesions. At this point in time the presentation is itchy eruptions with or without scarring.Spread
The MC can spread via touching, means it is contagious. This is the most common reason of more than one incidence of infection in the same house, class, or closed working groups. It can also spread faster with scratching and sharing common items. The spread also does not follow linear spread, it means it will only effect individuals having weaker immunity and bad skin hygiene.It also spreads via auto-inoculation especially in children who cant resist scratching and itching the lesions and touching other parts of body.
The MC virus is shed from skin and therefore, it does not spread via coughing, sneezing etc. As soon as lesions are healed, virus is completely removed but re-infection can occur if a person has same source of exposure and has lower immunity.
It may also present as an opportunistic infection in people with lower immunity such as in HIV, Cancer, having recurrent atopic dermatitis, etc.
 Diagnosis
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of MC is quite simple and straight forward. In majority of the cases it is diagnosed by clinical examination only. The careful observation of peculiar nature of eruptions yields clearcut diagnosis. In few cases where eruptions are either altered by super added infections, too much of scratching or atypical presentation, skin biopsy can be advised which clarifies the diagnosis.Differential Diagnosis
MC should be clearly differentiated from similar conditions such as Herpes, basal cell carcinoma, keratoacanthoma, histoplasmosis, coccidioidomycosis, and verruca vulgaris etc.Conventional Treatment
In conventional system of medicine, the aim of treatment is removal in broadly three different ways:- Physical removal via laser, cryotherapy, curettage etc.
- Oral therapy with drugs such as cimetidine or
- Local therapy with drugs such as Podophyllotoxin etc.
General Management
The general management with respect to MC are:- Maintain good hygiene especially of skin
- Avoid scratching
- Maintain body’s immunity in general
- Keep nails of children trim and clean
- Avoid outdoor activities which involves close contact such as swimming, sports, etc.
- Avoid sharing objects such as towels, handkerchief with other family members.
Role of Homeopathy in Molluscum Contagiosum
Homeopathy heals holistically!In general, the aim of Homeopathy is to stimulate the body’s inner strength and improve the overall immune system. The homeopathy also reduces the disease burden and improve overall health. The method, also known as individualised treatment, is considered the best method of treatment because it follows the holistic approach and not only alleviating the symptoms alone.
- The treatment not only involves removing the lesions but to reduce the tendency for re-infection.
- It also follows the rule to shorten the duration of symptoms and helps in removal of disease from its root cause.
- The prescription is dependent upon symptoms, signs, tendencies, history, and causation.
- The treatment can be curative, palliative, or supportive depending upon state and staging of disease.
- BROMIUM: When eruptions take pictures like acne and are pustule in nature. Boils like eruptions on arms and face. [Second line of remedy]
- MERCURIUS: Eruptions which are itchy, odorous, and moist in nature. General tendency to free perspiration. Vesicular and pustular eruptions. Itching, worse from warmth of bed. [First as well as second line of remedy]
- NITRIC ACID: Eruptions where there is bleeding, or which have a base like raw flesh. Exuberant granulations. Papules worse on forehead. [First line of remedy]
- SEPIA: Itching; not relieved by scratching; worse in bends of elbows and knees. Eruptions where super added infection is predominant, especially ringworm. Tendency for hyperhidrosis and bromhidrosis. Invaluable remedy in cases of young children and adults. [First line of remedy]
- SILICEA: Delicate, pale, waxy constitutions. Pus offensive. Every little injury or scratching suppurates. Eruptions itch only in daytime and evening. [Second line of remedy]
- SULPHUR: A very useful remedy to start as well as end a case of skin eruptions. Unhealthy skin with tendency for suppurations (primary or secondary infections). Itching, burning; worse scratching and washing. Pimply eruption and pustules. Pruritus, especially from warmth, in evening, often recurs in springtime, in damp weather. [First as well as second line of remedy]
Disclaimer
This article does not intend to replace the in-person consultation. The facts are for general purpose and public awareness only, and must not be taken as Medical Consultation in any form. For consultation, treatment and specific queries you need to contact your healthcare professional.Not for Medico-legal purposes.
©Public Health and Homeopathy Awareness Series (PHHA) by Vivid Homeopathy. The facts and information given in this article are for general purpose and public awareness only, and must not be taken as Medical Consultation in any form. Not for Medico-legal purposes.
For consultation, reprint request and collaborations please contact us.
 Effects on Health
Effects on Health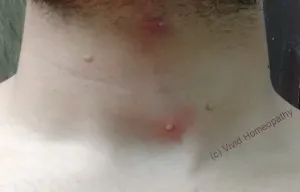 Diagnosis
Diagnosis